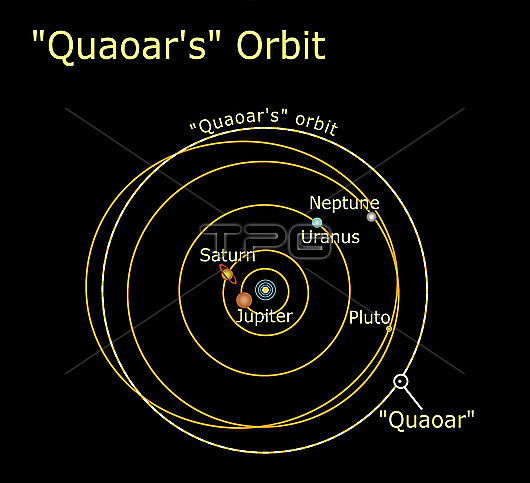
Illustration of Quaoar's (pronounced kwa-whar) orbit. Quaoar is the largest object discovered in the solar system since the discovery of Pluto 72 years ago. It was discovered by American astronomers Chad Trujillo and Michael Brown on 4th June 2002 at the Palomar Observatory, San Diego, USA. This dwarf planet is located 6.5 billion kilometres away from Earth in the Kuiper Belt, an icy debris field beyond Neptune containing small comet-like bodies. Quaoar measures 1300 kilometres in diameter. Researchers suspect it is composed mostly of low-density ices and rock, similar to a comet. Signs of crystalline ice on the surface of Quaoar have been detected with some surprise, as this is caused by the sublimation and refreezing of water. This would indicate that the temperature rose to at least -160 degrees Celsius (C) sometime in the last ten million years, from its natural temperature of -220 degrees C. The more widely accepted theory is that cryovolcanism occurred as a result of the decay of radioactive elements within Quaoar?™s core.
| px | px | dpi | = | cm | x | cm | = | MB |
Details
Creative#:
TOP28995692
Source:
達志影像
Authorization Type:
RM
Release Information:
須由TPG 完整授權
Model Release:
no
Property Release:
Right to Privacy:
No
Same folder images:

 Loading
Loading