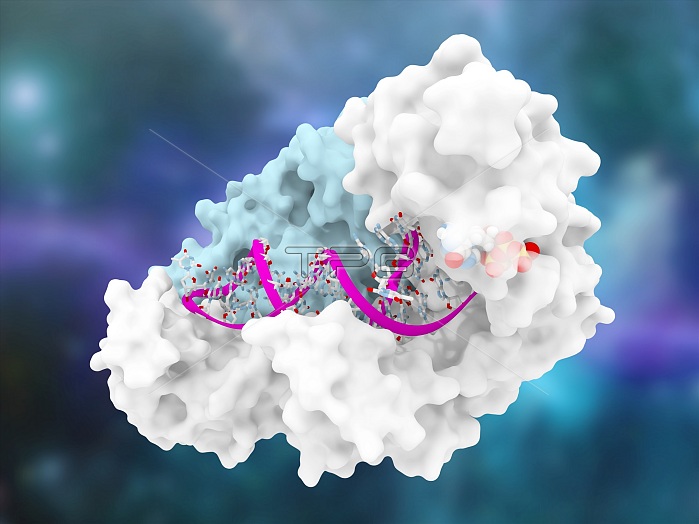
HIV-1 reverse transcriptase and drug delivery, illustration. The human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) single-stranded RNA genome is converted into double-stranded DNA by the viral reverse transcriptase (blue and white) and then the DNA is integrated in the DNA of an infected human cell. The reverse transcriptase is one of the main targets to disrupt the virus multiplication through an inhibitor. Here, the enzyme is from a mutated (resistant) form of HIV known as Q151M. The enzyme is shown bound to a DNA aptamer (helical molecule at centre), which is part of a drug delivery mechanism. The drug present here (partially seen at upper right) is Entecavir, used to treat hepatitis B (HBV) in patients with HIV.
| px | px | dpi | = | cm | x | cm | = | MB |
Details
Creative#:
TOP24702760
Source:
達志影像
Authorization Type:
RM
Release Information:
須由TPG 完整授權
Model Release:
N/A
Property Release:
N/A
Right to Privacy:
No
Same folder images:

 Loading
Loading