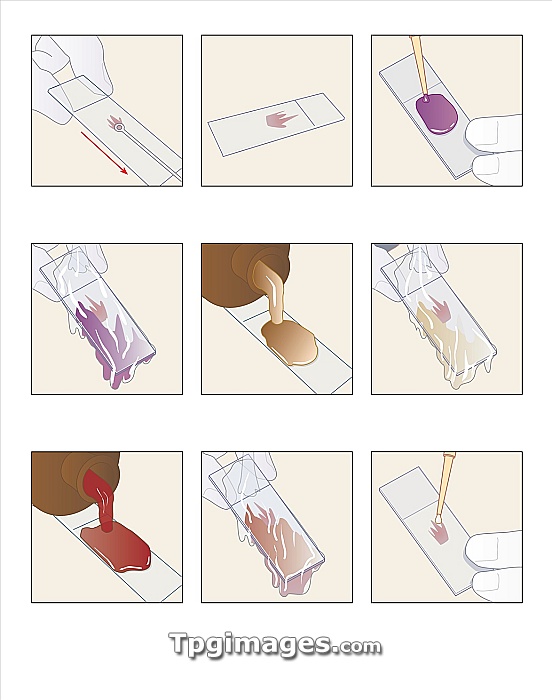
Gram staining procedure, artwork. Gram staining is used to differentiate between two groups of bacteria. Gram-positive bacteria are stained dark blue by the process, whereas Gram negative are unaffected. From top left to bottom right: 1) A sample of bacteria is smeared onto a glass slide. 2) The smear is dried slowly and heat-fixed to kill the bacteria. 3) The slide is flooded with gentian violet and left for 1 minute. 4) The gentian violet is washed off. 5) An iodine solution is added to aid penetration and retention of the stain. 6) After 30 seconds the slide is rinsed with ethanol, which washes the iodine out of some of the bacteria. 7) A red counter-stain (fuschin or eosin) is added to stain the Gram-negative bacteria. 8) The counter-stain is left for 30-60 seconds and then rinsed. 9) A drop of immersion oil is added to the slide, which is now ready to place under a microscope.
| px | px | dpi | = | cm | x | cm | = | MB |
Details
Creative#:
TOP07420228
Source:
達志影像
Authorization Type:
RM
Release Information:
須由TPG 完整授權
Model Release:
NO
Property Release:
NO
Right to Privacy:
No
Same folder images:

 Loading
Loading