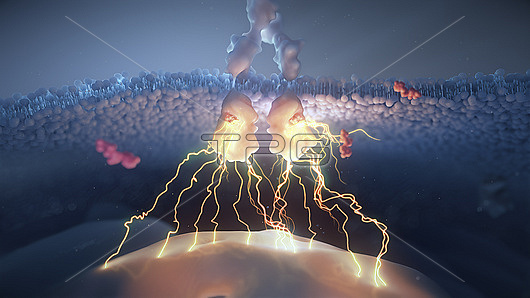
Illustration of a fibroblast growth factor receptor (FGFR) dimer over signalling in a cell. Fibroblast growth factor molecules (red) are bound to the receptor resulting in hyperactivity. The human fibroblast growth factor receptor family (FGFR1-4) regulates important biological processes including embryogenesis, angiogenesis (blood vessel formation), tissue homeostasis, and cell proliferation. Mutations in FGFRs that lead to constant activation of FGFR and its downstream signalling pathways are involved in a number of cancers. The hyperactivity promotes anti-apoptotic (programmed cell death) mechanisms and cell proliferation, ultimately contributing to tumour formation and growth.
| px | px | dpi | = | cm | x | cm | = | MB |
Details
Creative#:
TOP30088899
Source:
達志影像
Authorization Type:
RM
Release Information:
須由TPG 完整授權
Model Release:
N/A
Property Release:
N/A
Right to Privacy:
No
Same folder images:

 Loading
Loading