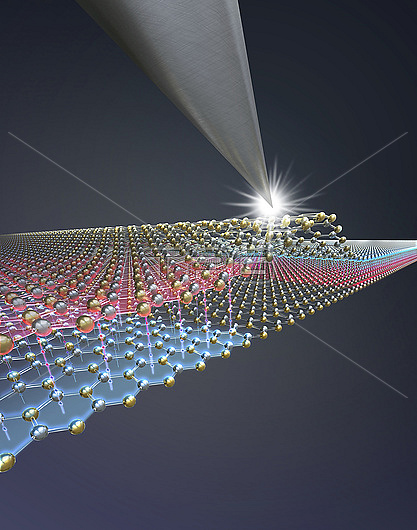
Nanoswitch. Illustration of the tip of an atomic force microscope (AFM) probing the upper layer of a single atom thick bilayer of hexagonal boron nitride (h-BN). Stacking atomic layers of this material in an unstable parallel orientation enables them to slide over each other, which allows local switching of polarisation. Such switching is used in the storage and retrieval of electronic data, making this material useful in efforts to further miniaturise electronic devices.
| px | px | dpi | = | cm | x | cm | = | MB |
Details
Creative#:
TOP29874556
Source:
達志影像
Authorization Type:
RM
Release Information:
須由TPG 完整授權
Model Release:
N/A
Property Release:
N/A
Right to Privacy:
No
Same folder images:
2d3dafmartworkatomicforcemicroscopybilayercgichemicalengineeringchemistrycrystallinedigitallygeneratedelectronicsh-bnhexagonalboronnitrideillustrationlatticematerialmetastablemolecualrmodelmolecularnanomaterialnanoswitchnanotechnologyno-onenobodynon-centrosymmetricorientationparallelpolarisationpolarizationprobeprobingscanningslidetronicsswitchingthreedimensionatiptwodimensionalutrathin
2d3dafmartworkatomicbilayerboroncgichemicalchemistrycrystallinedigitallydimensionadimensionalelectronicsengineeringforcegeneratedh-bnhexagonalillustrationlatticematerialmetastablemicroscopymodelmolecualrmolecularnanomaterialnanoswitchnanotechnologynitrideno-onenobodynon-centrosymmetricorientationparallelpolarisationpolarizationprobeprobingscanningslidetronicsswitchingthreetiptwoutrathin

 Loading
Loading