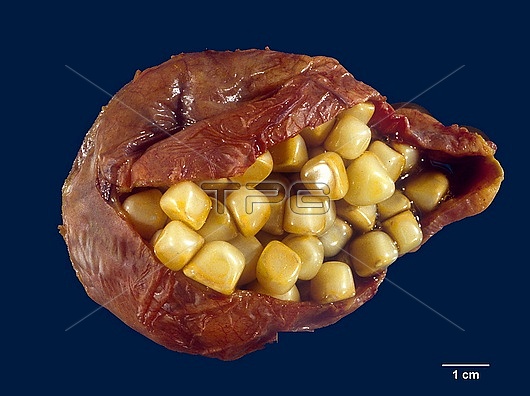
Multifaceted cholesterol gallstones in a gallbladder. Gallstones cause significant morbidity worldwide. They are responsible for more than 95% of biliary tract diseases. The incidence of gallstones is strikingly high in the native populations of North and South America (60-80%), presumably under genetic influences. In the US, 10-20% of adults have gallstone disease with a strong female predilection. In the Western countries, gallstones are predominantly cholesterol type. In Asia and Africa, they are mainly pigment type and associated with chronic haemolysis or biliary tract infections. Cholesterol stones can be small or large, single or multiple, round to ovoid, and pale yellow in colour. Pure cholesterol stones (100% cholesterol monohydrate) have a golden yellow colour, whereas mixed cholesterol stones are darker, greyish-yellow to brown due to increasing amounts of calcium carbonate, phosphates, and bilirubin. Cholesterol stones have a finely granular, hard external surface and a radiating crystalline or laminated interior. Facets develop when multiple stones form and grow within a confined space.
| px | px | dpi | = | cm | x | cm | = | MB |
Details
Creative#:
TOP29676082
Source:
達志影像
Authorization Type:
RM
Release Information:
須由TPG 完整授權
Model Release:
N/A
Property Release:
N/A
Right to Privacy:
No
Same folder images:

 Loading
Loading