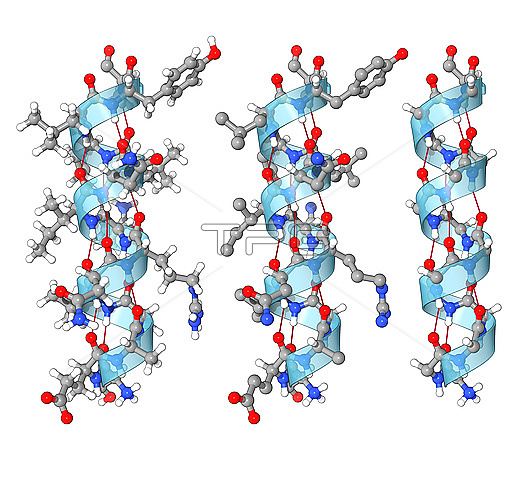
Illustration showing three alpha helices. This is a secondary structure formed from a protein's polypeptide chain of amino acids. This helical structure arises when the carbonyl group (a carbon atom double bonded to an oxygen atom) of one amino acid forms a hydrogen bond (red line) with the amino hydrogen atom of an amino acid four places down the chain. A complete alpha helix is shown at left, the same alpha helix without external side chain hydrogens is shown in the centre, and the same alpha helix without any side chains (backbone only) is shown at right.
| px | px | dpi | = | cm | x | cm | = | MB |
Details
Creative#:
TOP27990389
Source:
達志影像
Authorization Type:
RM
Release Information:
須由TPG 完整授權
Model Release:
N/A
Property Release:
N/A
Right to Privacy:
No
Same folder images:

 Loading
Loading