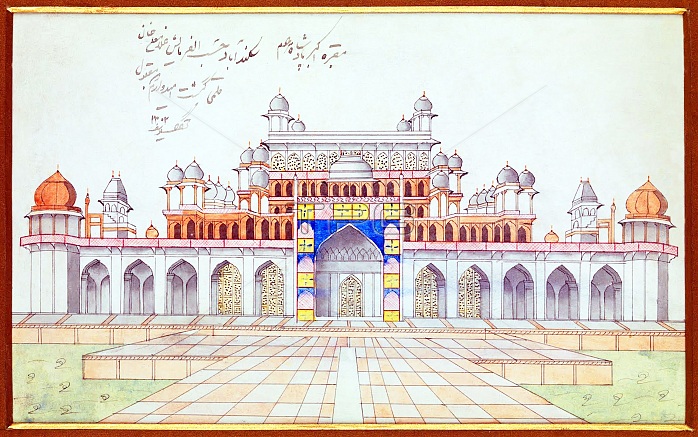
The Tomb of the the third Mughal Emperor Akbar (r. 1556-1605) is an important Mughal architectural masterpiece, built 1605-1613 and set in 48 Ha (119 acres) of grounds in Sikandra, a suburb of Agra, Uttar Pradesh, India. Emperor Akbar himself commenced its construction around 1600, according to Central Asian tradition to commence the construction of one's tomb during one's lifetime. Akbar himself planned his own tomb and selected a suitable site for it, after his death, Akbar's son Jahangir completed the construction in 1605-1613. The south gate is the largest, with four white marble chhatri-topped minarets which are similar to (and pre-date) those of the Taj Mahal, and is the normal point of entry to the tomb. The tomb itself is surrounded by a walled enclosure 105 m square. The tomb building is a four-tiered pyramid, surmounted by a marble pavilion containing the false tomb. The true tomb, as in other Mughal mausoleums, is in the basement. The buildings are constructed mainly from a deep red sandstone, enriched with features in white marble. Decorated inlaid panels of these materials and a black slate adorn the tomb and the main gatehouse. Panel designs are geometric, floral and calligraphic, and prefigure the more complex and subtle designs later incorporated in Itmad-ud-Daulah's Tomb.
| px | px | dpi | = | cm | x | cm | = | MB |
Details
Creative#:
TOP27177463
Source:
達志影像
Authorization Type:
RM
Release Information:
須由TPG 完整授權
Model Release:
No
Property Release:
No
Right to Privacy:
No
Same folder images:

 Loading
Loading