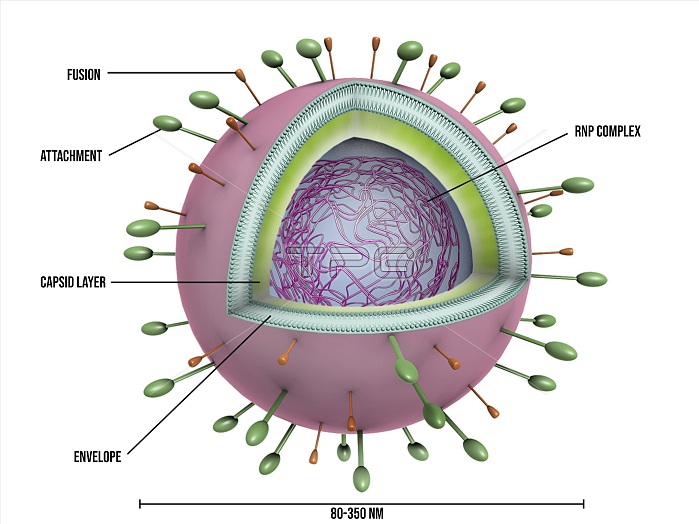
Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) particle, illustration. The internal core of the virus particle is shown here as a ribonucleoprotein (RNP) complex. This core is encased by a protein coat (the capsid, green) and then by an envelope of lipids (here labelled the envelope, blue with pink surface). Embedded in the envelope are surface proteins that bind to the host cell and play a vital role in the life cycle of the virus. The surface (spike) proteins shown here are fusion and attachment types, playing a role in the binding and fusing of the virus particle to a host cell. Viruses are very small, as shown by the scale bar (80 to 350 nanometres) at lower right. Human respiratory syncytial virus (HRSV) is a cause of respiratory tract infections.
| px | px | dpi | = | cm | x | cm | = | MB |
Details
Creative#:
TOP24703607
Source:
達志影像
Authorization Type:
RM
Release Information:
須由TPG 完整授權
Model Release:
N/A
Property Release:
N/A
Right to Privacy:
No
Same folder images:

 Loading
Loading