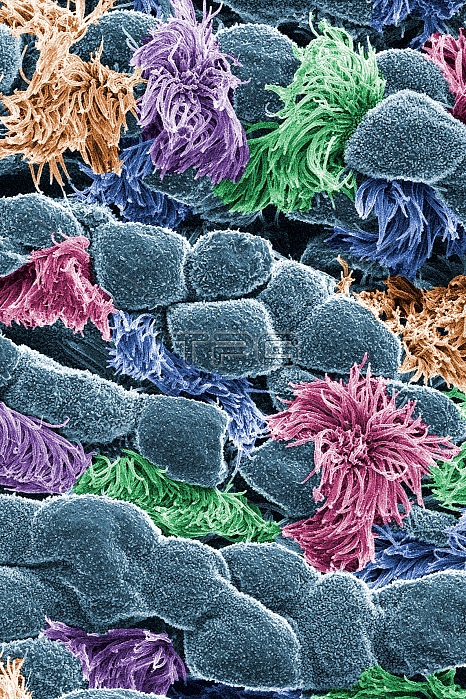
In this image, viewed with a ZEISS ORION NanoFab microscope, the community of cells lining a mouse airway is magnified more than 10,000 times. This collection of cells, known as the mucociliary escalator, is also found in humans. It is our first line of defense against inhaled bacteria, allergens, pollutants and debris. Malfunctions in the system can cause or aggravate lung infections and conditions such as asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. The cells shown in gray secrete mucus, which traps inhaled particles. The colored cells sweep the mucus layer out of the lungs. Epithelium is one of the four basic types of animal tissue, along with connective tissue, muscle tissue and nervous tissue. Epithelial tissues line the cavities and surfaces of structures throughout the body, and also form many glands. Functions of epithelial cells include secretion, selective absorption, protection, transcellular transport and detection of sensation. The airway comprises those parts of the respiratory system through which air flows, from inhalation at the nose or mouth, to termination in the alveoli. It is generally used synonymously with respiratory tract. The airway is usually described as being divided into an upper and a lower airway, the division being marked by the larynx.
| px | px | dpi | = | cm | x | cm | = | MB |
Details
Creative#:
TOP22234211
Source:
達志影像
Authorization Type:
RM
Release Information:
須由TPG 完整授權
Model Release:
N/A
Property Release:
No
Right to Privacy:
No
Same folder images:

 Loading
Loading