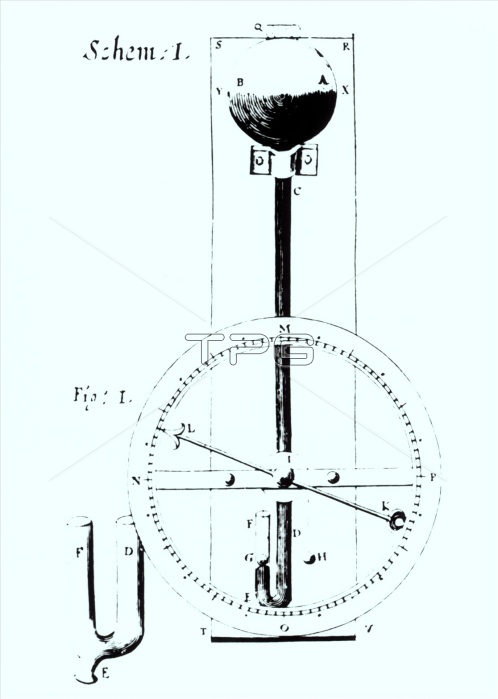
Wheel barometer. Drawing of a wheel barometer in Micrographia (1665) written by the British physicist Robert Hooke (1635-1703). The barometer was used to measure air pressure. Mercury filled a glass tube (at centre) which is open at one end (marked 'F') and has a sealed bulb (at centre top) at the other. In the bulb a vacuum provides enough suction to prevent the mercury from flowing out of the tube. The open end of the tube contains a ball which floats on the mercury. The float is attached to the pointer by a length of string. If air pressure rises the mercury is forced up into the bulb and the level of the mercury at the open end drops. As the float drops too, the pointer moves.
| px | px | dpi | = | cm | x | cm | = | MB |
Details
Creative#:
TOP10242335
Source:
達志影像
Authorization Type:
RM
Release Information:
須由TPG 完整授權
Model Release:
N/A
Property Release:
N/A
Right to Privacy:
No
Same folder images:

 Loading
Loading