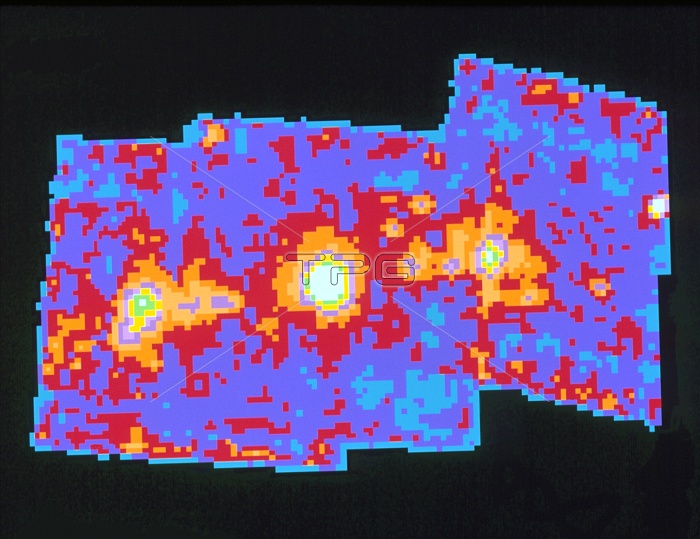
X-ray image of SS 433, a black hole candidate, taken by the Einstein Observatory satellite. SS 433 is the central white spot. It is believed to consist of a normal star whose outer gases are falling onto a compact companion star (a neutron star or a black hole) in a spiralling accretion disc. This whirling disc's hot gases generate intense X-ray emission. The disc also emits clouds of hot gas, which shoot out on either side like jets of spray from a garden sprinkler. The jets are the bright areas on either side. The colours are coded for X-ray intensity, from white for the most intense to blue for the least intense.
| px | px | dpi | = | cm | x | cm | = | MB |
Details
Creative#:
TOP10240545
Source:
達志影像
Authorization Type:
RM
Release Information:
須由TPG 完整授權
Model Release:
N/A
Property Release:
N/A
Right to Privacy:
No
Same folder images:

 Loading
Loading