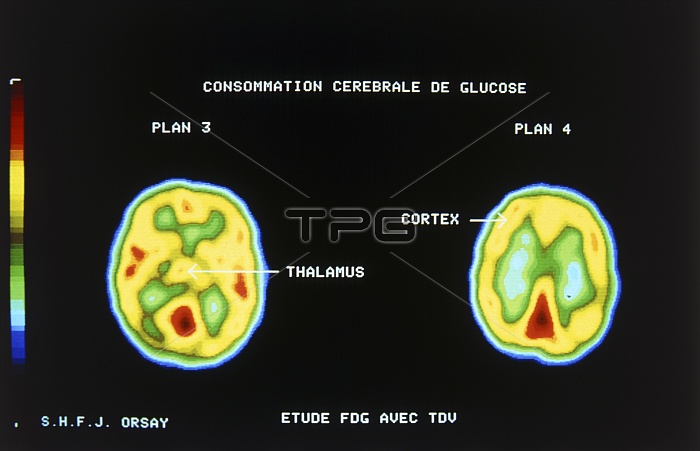
Two axial images of the brain obtained by Positron emission tomography (PET) showing the utilisation of glucose by tissues at different levels in the brain. PET gives functional details of body tissues by mapping the location of a tracer (FDG - an analogue of glucose) labelled with a positron-emitting radionuclide. Positrons annihilate on formation with nearby electrons to produce 2 gamma rays that fly off at 180 degrees to each other. This phenomena allows a fairly exact location of the tracer to be mapped: both gamma rays from an annihilation strike a crystal detector and resulting data are processed to give the colour coded images.
| px | px | dpi | = | cm | x | cm | = | MB |
Details
Creative#:
TOP10219153
Source:
達志影像
Authorization Type:
RM
Release Information:
須由TPG 完整授權
Model Release:
N/A
Property Release:
N/A
Right to Privacy:
No
Same folder images:

 Loading
Loading