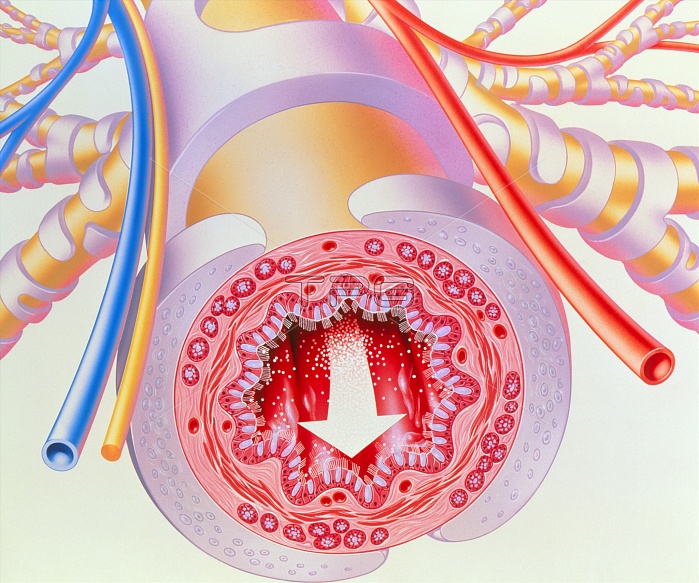
Bronchodilators in asthma. Illustration of an inhaled bronchodilator drug passing through a constricted bronchiole of a lung. The structure of the bronchiole is shown in section. Its inner wall is lined with ciliated epithelium containing mucus-secreting goblet cells (grey). Under this a layer of fibro-elastic connective tissue (pink); smooth muscle tissue (red), which controls the airway's diameter; and submucosal connective tissue containing mucus glands. Incomplete rings of cartilage surround the wall of the bronchiole. Asthma is an allergic reaction that causes constriction of the bronchioles, resulting in wheezing and breathlessness.
| px | px | dpi | = | cm | x | cm | = | MB |
Details
Creative#:
TOP10195414
Source:
達志影像
Authorization Type:
RM
Release Information:
須由TPG 完整授權
Model Release:
N/A
Property Release:
N/A
Right to Privacy:
No
Same folder images:

 Loading
Loading