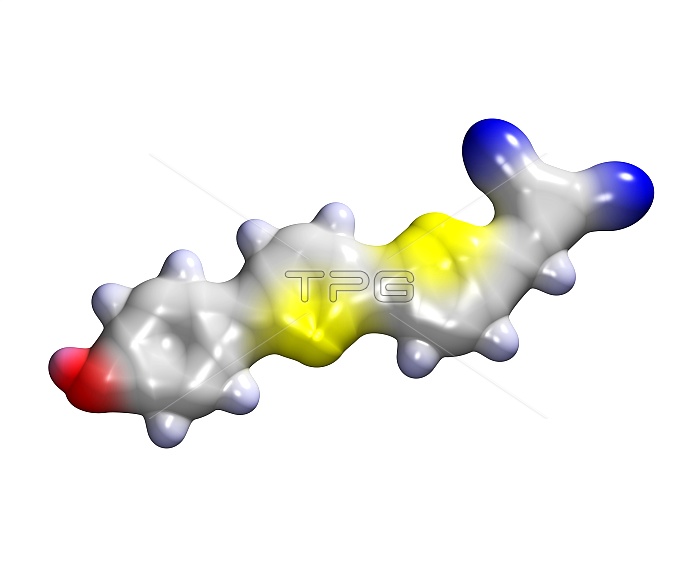
NIAD-4 Alzheimer's disease marker dye, molecular model. This chemical was developed in 2005 as a diagnostic marker for Alzheimer's disease. When injected into the brain it specifically binds to the plaques of amyloid protein that are characteristic of the disease. Shining near- infrared light at the brain causes the NIAD-4 to fluoresce, and the emitted light can then be detected to provide a map of the affected brain areas. This could lead to much earlier diagnosis of the condition, and provide information on how the disease progresses. The surface of the molecule's electron cloud is shown here, with the underlying atoms colour-coded: carbon (grey), hydrogen (pale blue), nitrogen (dark blue), oxygen (red) and sulphur (yellow).
| px | px | dpi | = | cm | x | cm | = | MB |
Details
Creative#:
TOP10164543
Source:
達志影像
Authorization Type:
RM
Release Information:
須由TPG 完整授權
Model Release:
N/A
Property Release:
N/A
Right to Privacy:
No
Same folder images:

 Loading
Loading