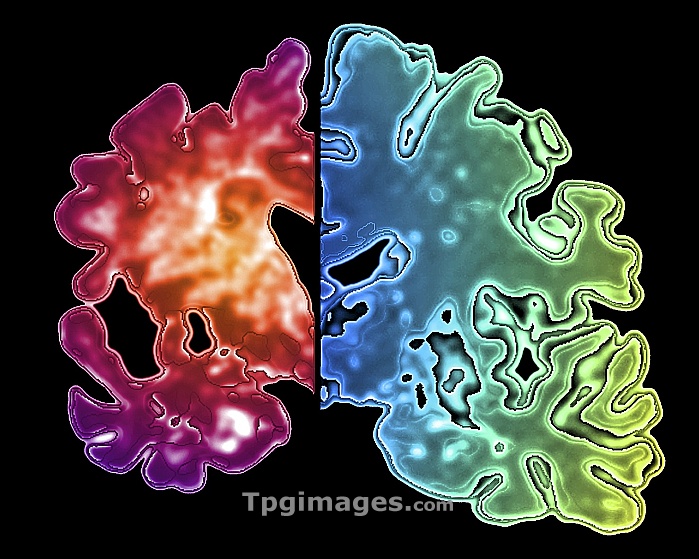
Alzheimer's brain. Computer graphic of a vertical (coronal) slice through the brain of an Alzheimer patient (at left) compared with a normal brain (at right). The Alzheimer's disease brain (red) is considerably shrunken, due to the degeneration and death of nerve cells. Apart from a decrease in brain volume, the surface of the brain is often more deeply folded. Tangled protein filaments (neurofibrillary tangles) occur within nerve cells and patients also develop brain lesions of beta- amyloid protein. Alzheimer's disease accounts for most cases of senile dementia. Symptoms include memory loss, disorientation, personality change and delusion. It ultimately leads to death. .
| px | px | dpi | = | cm | x | cm | = | MB |
Details
Creative#:
TOP07423063
Source:
達志影像
Authorization Type:
RM
Release Information:
須由TPG 完整授權
Model Release:
NO
Property Release:
NO
Right to Privacy:
No
Same folder images:

 Loading
Loading